速寫 Day49
來源:赤倉
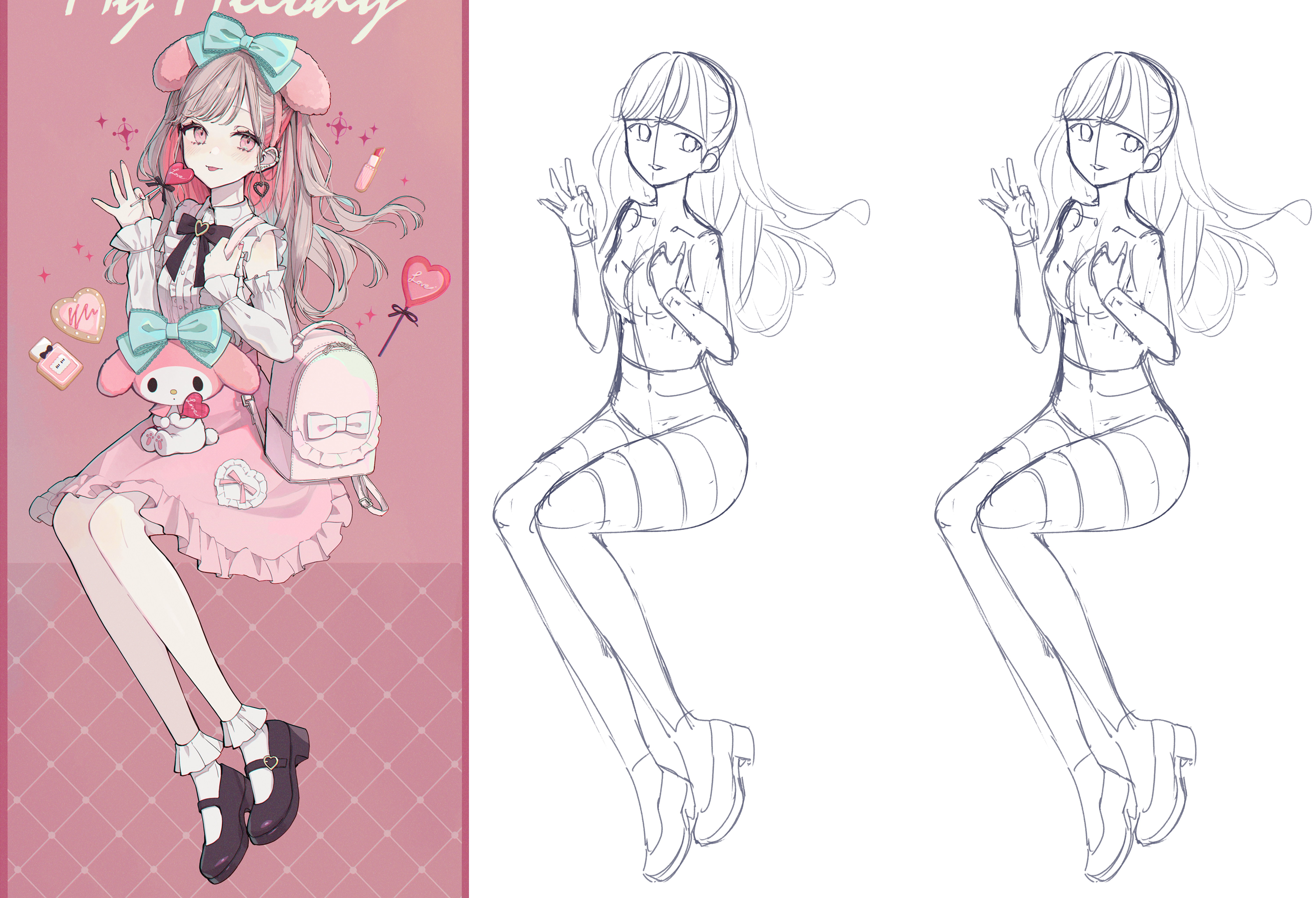
瑪奇瑪草稿,沒動ㄏㄏ

今天在準備搬家,
打包走人,
登出交大。
所以今天沒甚麼時間速寫ㄌ ㄏㄏ
而且感覺到裝潢完全結束之前,
這陣子應該不常更新了。
但書還是要照唸,
動畫還是要照看。
嘻嘻。
今日日文單字:
日文文法 ─ 四篇文章
- Vようとする/としている=これから始める ─ 從現在開始V
- ゆえに ─ 因為
- ないかぎり/ないと ─ 如果不…的話
- 耳にする/聞く ─ 聽
- なりの ─ 像是、正如
- それにしても ─ 話說、但是
- (だけ)にとどまらず、…にも ─ 不僅只
- AをBという ─ A也被稱作B
- Vよう心掛(が)ける ─ 往V努力
- いかに…であろうと ─ 不管有多麼
- ところが ─ 但是
- AがBも ─ 主A副B
- としか言いようがない ─ 實在是
- かぎり ─ 只限
稍微的筆記
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning ─ Bishop
Probability Theory
Bayes’ theorem: \(p(Y|X)=\dfrac{p(X|Y)p(Y)}{p(X)}\)
The denominator can be expressed as: \(p(X)=\sum_Yp(X|Y)p(Y)\)
Prior probability: probability available before we observe.
Posterior probability: probability obtained after we have observed. (given some events.)
-> Bayes’ theorem was used to convert a prior probability into a posterior probability by incorporating the evidence provided by the observed data.
-> The quantity \(p(X|Y)\) where X implys the observed data set can be viewed as a function of the parameter vector function \(Y\), in which case it is called the likelihood function.
-> Express how probable the observed data set is for different settings of the parameter vector \(Y\).Bayes’ theorem: \(p(Y|X)=\dfrac{p(X|Y)p(Y)}{p(X)}\)
\(Posterior\propto likelihood\times prior\)
Maximum likelihood: in which \(Y\) is set to the value that maximizes the likelihood function \(p(X|Y)\)
-> The negative log of the likelihood function is called an error function. Because negative log is a monotonically decreasing function, maximizing the likelihood is equivalent to minimizing the error.
–
- 令 \(x=g(y)\)
- \(p_y(y)=p_x(x)|\dfrac{dx}{dy}|=p_x(g(y))|g^{’}(y)|\)
The Gaussian distribution
- \(N(x|\mu,\sigma^2)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi \sigma^2}}exp(\dfrac{-(x-\mu)^2}{2\sigma^2})\)
- \(\beta=1/\sigma^2\), which means the reciprocal of the variance, so called precision.
- We can use the maximum likelihood method to obtain the sample mean and variance.
-> However, the maximum likelihood approach systematically underestimates the variance of the distribution, which is a phenomenon called bias and is related to the problem of over-fitting.
-> \(E[\sigma_{ML}^2]=(\dfrac{N-1}{N})\sigma^2\) , because the variance is measured relative to the sample mean and not relate to the true mean.
–
- Training data set: \((x,t)\)
- Weight:\(w\)
- Precision:\(\beta\)
- We can express our uncertainty over the value of the target variable using a probability distribution.
-> \(p(t|x,w,\beta )=N(t|y(x,w),\beta^{-1})\)
-> Use maximum likelihood method to obtain \(W_{ML}\space and\space \beta_{ML}\), then:
-> \(p(t|x,w_{ML},\beta_{ML} )=N(t|y(x,w_{ML}),\beta_{ML}^{-1}\)
–
- Now let \(\alpha\) be the precision of the distribution, which is so called hyperparameters as those variables control the distribution of *model parameters. Then, by Bayes’ theorem:
-> \(p(w|x,y,\alpha, \beta )\propto p(t|x,w,\beta )\times p(w|\alpha )\)
-> We can determine \(w\) by maximizing the posterior distribution, and this technique is called MAP (Maximum posterior).
-> Finally, we can conclude that maximizing the posterior distribution is equivalent to minimizing the regularized sum-of-squares error function with a regularization parameter given by \(\lambda=\dfrac{\alpha}{\beta}\)
今日其他進度:
- 日文N1文法、N1題目
- 一堆的動畫
我會繼續努力的。